If you are a database developer or admin, then the SELECT INTO TEMP TABLE and INSERT INTO TEMP TABLE will be almost your everyday task. This article will help you explore the SELECT INTO and INSERT INTO TEMP TABLE in detail.
The SELECT
INTO TEMP TABLE is a simple method of creating a new table and copying the data from
the source table. The SELECT INTO TEMP TABLE does the following operations
internally.
- Creates a new table like the source table with the exact same column with data type
- Reads and inserts to the new table from the source table
SELECT INTO TEMP TABLE Statement
The SELECT INTO TEMP TABLE is used to create a new table and copy the data over to either a user table or a temporary table.
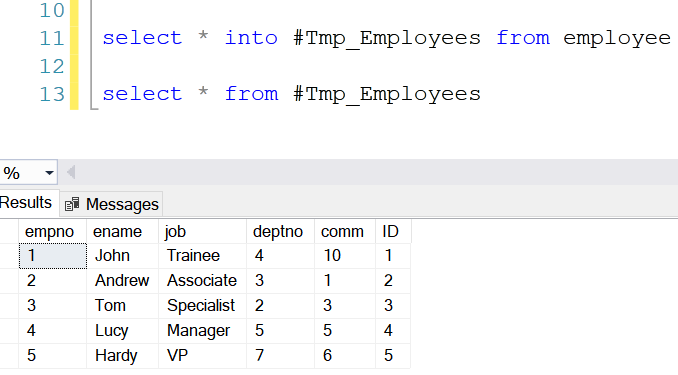
select * into #Tmp_Employees from employee
The above
example will insert all records into the #Tmp_Employees temporary table from the employee
user table.
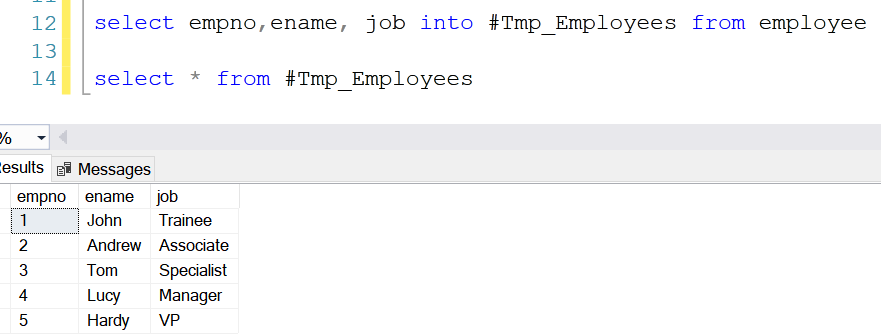
Suppose we
want to insert specific columns of the employees' table into the temporary
table, then we must specify the column names in the SELECT INTO statement.
select empno,ename, job into #Tmp_Employees from employee
In both
the examples of select into with * and with specific columns, the column name
remains the same as the source table.
INSERT INTO TEMP TABLE Statement
Again, the INSERT INTO TEMP TABLE statement is used to insert the source table data into the temporary table. In this case, the table creation will have to be manually created by the user. The SQL Server does not involve creating the temporary table internally.
INSERT INTO statement can be used either for inserting into an existing user table, or a newly created temporary table.
The below example illustrates the insertion of all columns into a temporary table from the employee table.
create table #Tmp_Employees
(
empno int,
ename varchar(100),
job varchar(100),
deptno smallint,
comm smallint,
ID int
)
insert into #Tmp_Employees
select * from employee
The statement selects all columns with the help of a * from the employee table and inserts it into #Tmp_Employees temporary table.
The below example illustrates the insertion of particular columns into a temporary table from the employee table.
insert into #Tmp_Employees (empno, ename, job)
select empno, ename, job from employee
The statement selects just empno, ename, job columns from employee table and inserts them into #Tmp_Employees temporary table.
SELECT INTO Vs INSERT INTO TEMP TABLE Statement
- SELECT INTO creates a destination temporary table automatically. It reads data from the source table and inserts it into the temporary table.
- INSERT INTO doesn’t create a destination temporary table automatically. We have to explicitly insert it into the existing user table or a temporary table from the source table.
Performance Metrics
Starting
from SQL Server 2014, the SELECT INTO performance has shown better. This is
because the statements have been running parallel to improve performance. However,
through the course of my experience, here is my take below.
SELECT
INTO works well if the columns to create are lesser. If the number of columns
increases with complex logic underlying, the SELECT INTO performance degrades.
INSERT INTO
works well if the columns to be inserted are more.
In
general, the SELECT INTO performance is better than the INSERT INTO. Be sure of the
number of columns you are supplying in both SELECT INTO and INSERT INTO statements.
Bottomline
In this
article, we have learned about the difference between the SELECT INTO and INSERT
INTO statements. In a practical environment, both methods are extensively
used based on the scenario. Use them in appropriate conditions to get the best
results or performance.
More articles for your reference:
Difference Between Shared Lock, Exclusive Lock And Update Lock In SQL Sever
Difference Between Truncate and Delete Command in SQL Server









0 comments:
Post a Comment