The DIRTY_PAGE_POLL is a wait type that behaves like CHECKPOINT_QUEUE. This wait type was introduced in SQL Server 2012 with an indirect checkpoint feature. In most cases, the DIRTY_PAGE_POLL wait type can be ignored, it becomes important for all DBAs to have a basic idea of this wait type when it gets generated.
What is the DIRTY_PAGE_POLL Wait Type?
The DIRTY_PAGE_POLL
wait type is a background wait that is related to the recovery writer process
that is used by the indirect checkpoint feature. The wait type runs continuously
in the background of your SQL Server instance.
The
checkpoint process inside the SQL Server is accountable for writing modified
data pages from the buffer cache to the database data files on disk. The automatic checkpoint
process runs regularly at a set interval of 1 minute. However, the indirect
checkpoint feature will allow you to configure a specific checkpoint interval
at the database level.
The checkpoint process is very important in the recovery of a SQL Server database when any crash happens.
Case Scenario:
Suppose
you were working on a SQL Server instance and suddenly your server crashed. Fortunately,
with a simple restart of SQL Server service, all gets back to normal. The first
thing the SQL Server does is to start a recovery process. The recovery process
checks for the transaction log for uncommitted transactions when the crash occurred
and performs a rollback of the transaction.
The recovery
process checks whether any data pages that were modified but only at the buffer
cache level. If there were any transactions in the buffer cache, then such transactions
will be redone by the SQL Server from the transaction log. A busy server will have
such transactions where a lot of them were trapped in the buffer cache level. In
such cases, the recovery time will be more than normal.
Because of
the same, from SQL Server 2012 a new feature was introduced "Target Recovery
Time" which you can see in the database properties. By configuring this
feature, we can tell SQL Server to write the modified data pages to disc faster.
An example of the database properties with the "Target Recovery Time" is shown below.
Feature at the database level:
A sample
example of the database properties with the "Target Recovery Time" is shown below.
In the image, the Target Recovery Time option is configured to 0 by default. If the value is 0, then the indirect checkpoint is not being used. If the value is anything greater than 0, an indirect checkpoint will start to happen as per the specification.
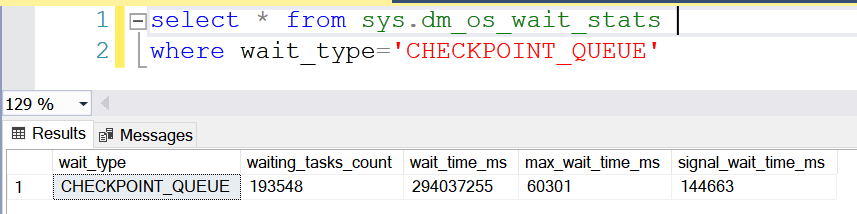
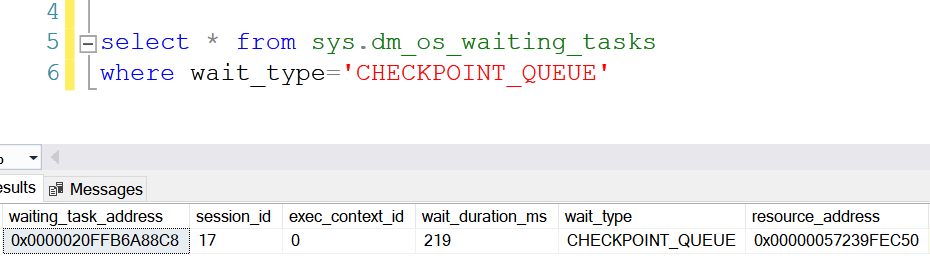
The wait type can be queried from sys.dm_os_wait_stats wait type.
Note: Starting from SQL Server 2016, the Target Recovery Time value is set to 60 seconds by default when you create a new database inside the SQL Server instance. In case you are manually changing to a new value of its own, then do not set the option to a low value. A value of less than 60 seconds can impose an extra load on the storage subsystem. This is because the SQL Server will start writing dirty pages continuously to disk. Be very wise while setting the value in the production environment.
Bottomline:
The DIRTY_PAGE_POLL wait type was introduced in SQL Server 2012. It was an introduction to the indirect checkpoint feature. Starting from SQL Server 2016, the default value was set to 60 for new database creation. The wait type will still get generated in case you are using the feature. The whole point is that the wait type values are for information only and do not impose any performance overhead.