DBAs are very much into using the DBCC
commands. The DBCC (Database Console Commands) statements are used for various
purposes like maintenance tasks, informational gathering, validation, and
miscellaneous tasks. I was working on importing data from one database to
another as part of my client’s requirement, and I had to insert the DBCC
results into a table.
Most often we as DB professionals tend to
just execute the DBCC commands and move on. But there are some instances where
we would require the results to be stored into a table. A simple DBCC code can
help us fetch the results to resemble that of fetching from a user-table.
Here is how you can insert the DBCC results
into a table. Please follow the steps as:
Step 1: Create a temp table as per the DBCC
result sets – DBCC SQLPerf(logspace)
While creating the temp table, please make
sure that the table definition is matching with the DBCC command’s output as
they can end with another error – Number of supplied values doesn’t match the table
definition.
Before creating the table definition, please
check for the DBCC results. The output number of columns is the one we are focusing
on:
EXEC('DBCC SQLPERF(LOGSPACE);')
Once we are clear that there are 4 columns to create from the output in our example here, please proceed to create the table structure as per the instructions below.
create table
#Temp_LogSpace
(
[DATABASE_NAME] nvarchar(100),
[LOGSIZE_MB] float,
[LOGSPACE_USED] float,
[LOGSTATUS] bit
)
insert
#Temp_LogSpace([DATABASE_NAME],
[LOGSIZE_MB], [LOGSPACE_USED],
[LOGSTATUS])
EXEC('DBCC
SQLPERF(LOGSPACE);')
Step 3: Select the data from temp table (#Temp_LogSpace)
after insertion
Step 1: Create a temp table as per the DBCC
result sets – DBCC Tracestatus()
Please check the results before creating the temp table.
EXEC ('DBCC
TRACESTATUS ();')
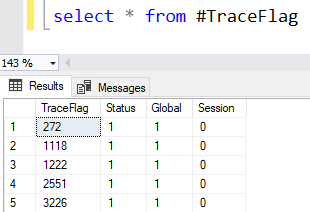
Create table
#TraceFlag
(
[TraceFlag] varchar(50)
,[Status]
bit
,[Global]
bit
,[Session]
bit
)
Step 2: Insert the DBCC results into a temp
table (#TraceFlag) using the EXEC ('') command
insert into
#TraceFlag
EXEC ('DBCC
TRACESTATUS ();')
Further, you can as well try to import data from any DBCC statements into a table and check the results. Once you transfer data to a temp table or a user-table, it’s your game to play with the data as per your requirement.
Related interesting topics for you:
"Different between clustered and non-clustered index"
"What is mdf, ndf, ldf"










0 comments:
Post a Comment