IDENTITY Property is a feature used with
the CREATE or ALTER TABLE commands and is used to generate unique values for a
column. The main reason behind using IDENTITY property is to keep the columns
unique.
Generally, in the industry’s production
environment, when the tables are highly loaded, there are high chances the data
can just get mixed up. An IDENTITY property on a table can simply be easy to
identify the column even on a table holding thousands of records.
General Syntax:
IDENTITY [ (seed ,
increment) ]
Seed – Seed is the value assigned to the
initial row for a table
Increment – Increment is the value assigned
to the IDENTITY value that will be an incremental addition to the previous row
count
The value passed default when seed and the increment are not assigned while creating IDENTITY property is (1,1).
A common error encountered before fixing the IDENTITY RESEED is as below:
Step 1: Create a table as [IDENTITY_TEST]
create table
[IDENTITY_TEST]
(ID int identity(1,1) not null,
number int,
subnumber int
)
Step 2: Insert records into [IDENTITY_TEST] table
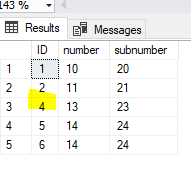
Step 3: Check the max of ID on [IDENTITY_TEST] table
select max(ID) from
IDENTITY_TEST
Step 4: Check IDENTITY column value
select IDENT_CURRENT('IDENTITY_TEST')
Here the identity scope value should be 6 but is giving an output as 2. The reason could be multiple and is mentioned at the end of the article.
Step 5: Reset IDENTITY SCOPE to the current max
ID value
DBCC CHECKIDENT ('IDENTITY_TEST', RESEED, 6);
If you would notice that the IDENTITY property was anonymously set to ID=2. The possible reasons for IDENTITY property to go out of order are when any one of below happens on your table:
1. Server restart or Database
failure – this is part of the SQL Server’s performance reasons where the Identity
value gets cached.
2. When there is a BULK LOAD on your
table.
3. Heavy DML transactions (Insert/Update/Delete
operation).
4. Transaction replication out of
Synch.
5. If a transaction is initiated
and left uncommit.
Note: Some of the IDENTITY scope values being cached to the older numbers are moreover unavoidable and has to be manually reset with the above steps.
You may also refer: 'Steps to add/remove identity property in SQL Server'












0 comments:
Post a Comment