I have seen a lot of times, people get confused to differentiate
the Truncate and Delete commands in SQL Server. If you are a DB developer or a
DBA, then this is a mandated requirement to know exactly what is being
performed when Truncate on a table and delete on a table. Let’s check the
difference between Truncate and Delete in SQL Server.
TRUNCATE
TRUNCATE is a DDL command, which is used to delete all the rows
of a table without being to use a WHERE clause. Most of them come up with an assumption
that a truncate cannot be rolled back once the TRUNCATE command is executed.
But, the assumption is very untrue! The TRUNCATE command can be rolled back
with the lopping into a begin transaction and rollback commands.
Further, in truncation, the pages are completely deallocated and commit to the transaction log as deallocation. TRUNCATE can be only executed
if login is given with an ALTER permission for a database. Additionally, as
the rows are completely removed from the table, there is less utilization in
the transaction log, hence performance is high.
Before we proceed with the truncation of the table, let’s create
a dummy table, insert some values on CusName and CusID, and test on it.
Create table dummy
(
CusID int not null,
CusName nvarchar(100) null
)
Insert into dummy values (1, 'Dale'), (2, 'James')
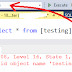
T-SQL command to truncate a table.
begin tran
Truncate table dummy
select * from dummy
rollback
The above command will completely remove two rows with two
unique records from the dummy table.
DELETE
DELETE is a DML command, which is used to either remove all
the rows from a table or a specific row from a table using the WHERE clause. As
the rows are deleted from the table one by one, every single delete from the
table is maintained and recorded in the transaction log. Since such records are
maintained, there is high utilization of transaction log, due to which the
performances are low.
Further, there is a need to DELETE permission for login in
SQL Server to carryout the DELETE command. When there is a rollback possibility
for Truncate, there is also a similar way to rollback DELETE records of a table
by looping to Begin Transaction.
T-SQL command to delete a table.
Let’s use the dummy table to delete the CusID record.
begin tran
DELETE from dummy where
CusID=1
select * from dummy
The above delete command will just delete the row selected
in the WHERE clause with CusID=1.